Extended
Events were first introduced in SQL Server 2008, and therefore you will not
face any problem implementing them in our environment.
Extended Events is a lightweight performance monitoring
feature that enables users to collect data to monitor and troubleshoot
problems.
A deadlock is a situation
where two or more processes or threads are blocked indefinitely, waiting for
each other to release resources that they need to proceed.
Here we
are going to observe how to gather deadlock information through Extended Events :
Creating SQL Server
Extended Events to Capture Deadlocks using Management Studio
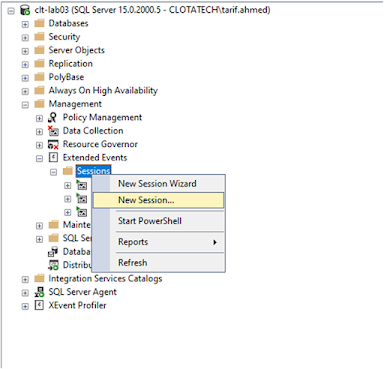
Step 1: First, open SQL Server Management
Studio (SSMS) and navigate to Management > Extended
Events > Sessions.
Step 2: Right-click on Sessions and select New
Session.
Step 3: In the new window, provide a name for your event, we will call it SQLWATCH_deadlock in this case. Select the event to start at the beginning of the server and when the session is created, you can change these settings if necessary.
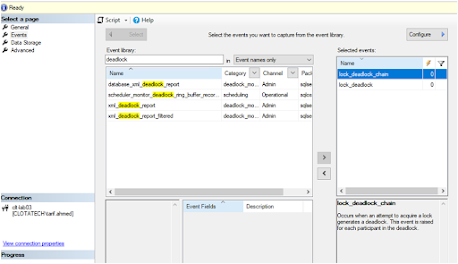
Step 4: Go to the Events tab and in the event
library textbox type “deadlock” to filter deadlock events:
Step 5: We will select 2 events: Lock_Deadlock (Raised when a request to acquire a lock is cancelled for the victim of a deadlock) and Lock_deadlock_chain
(Raised when a request to acquire a lock results in a deadlock. This event is raised for all members of the deadlock).
Step 6: Having both the events chosen, click on the
configure button, and a new window will be opened, in this window we will take
a snapshot of the sql_text field so that we can view the query that generated
the deadlock
Step 7: In the Data Storage tab, select where you want
to store the Extended Event data use a file.
Step 8: After that, click on OK to save the Event configuration, we can see that the
event is created and is already running.